SMS Blog
From Risk to ROI: 6 Data Security Techniques in the GenAI Age
In many of our previous blogs we have explored how introducing AI into your organization improves efficiency, reduces operational costs and drives meaningful business growth. As organizations explore the deployment of AI, it is critical to understand the range of available security models. Each model offers a different balance of risk, flexibility, and return on investment, and selecting the right approach depends on the specific context and requirements of your organization.
In this blog, we will take a deep dive into the security and protection of intellectual property in the context of AI adoption. We will highlight key strategies and best practices that you can apply within your organization. These insights are especially relevant to organizations across industries such as healthcare, nuclear energy, research, medical, finance, defense, and law, where data security is non-negotiable.
Different Strategies for Different Environments
The techniques described below may or may not be appropriate for your environment depending on your specific use case, the sensitivity of your data, and your compliance requirements.
For example, in Adam, our AI-powered knowledge base system, we implemented strict access controls requiring explicit approval for data access and designed the system to easily switch between third-party and self-hosted AI models. This enabled rapid adoption while maintaining strong data governance. However, while building Adam we made a deliberate trade-off: Adam is not suitable for processing controlled unclassified information (CUI) as it communicates with third-party systems not authorized for such access. For our use case, this is an acceptable compromise. You can read more about Adam’s security features in detail in our previous blog.
Similarly, you can reference the list of techniques mentioned here to evaluate and select the security measures that best align with your goals and organization’s needs.
1. Obfuscation of Contextual Data
Obfuscation involves transforming or masking sensitive elements within your input data before passing it to the AI system. For example, customer names might be replaced with pseudonyms, internal document references redacted, or private identifiers hashed. The goal is to preserve enough context for the AI to generate useful responses without revealing sensitive information.
This approach can enable organizations to use powerful third-party AI models, including public APIs, without directly exposing proprietary or regulated data. However, obfuscation has limits. If the model relies heavily on deep contextual understanding, altering the data too aggressively can reduce accuracy and effectiveness. Moreover, advanced models may still infer sensitive patterns or relationships from anonymized data. Obfuscation should be seen as a risk mitigation technique, not a comprehensive security solution. It works best when combined with other security measures.
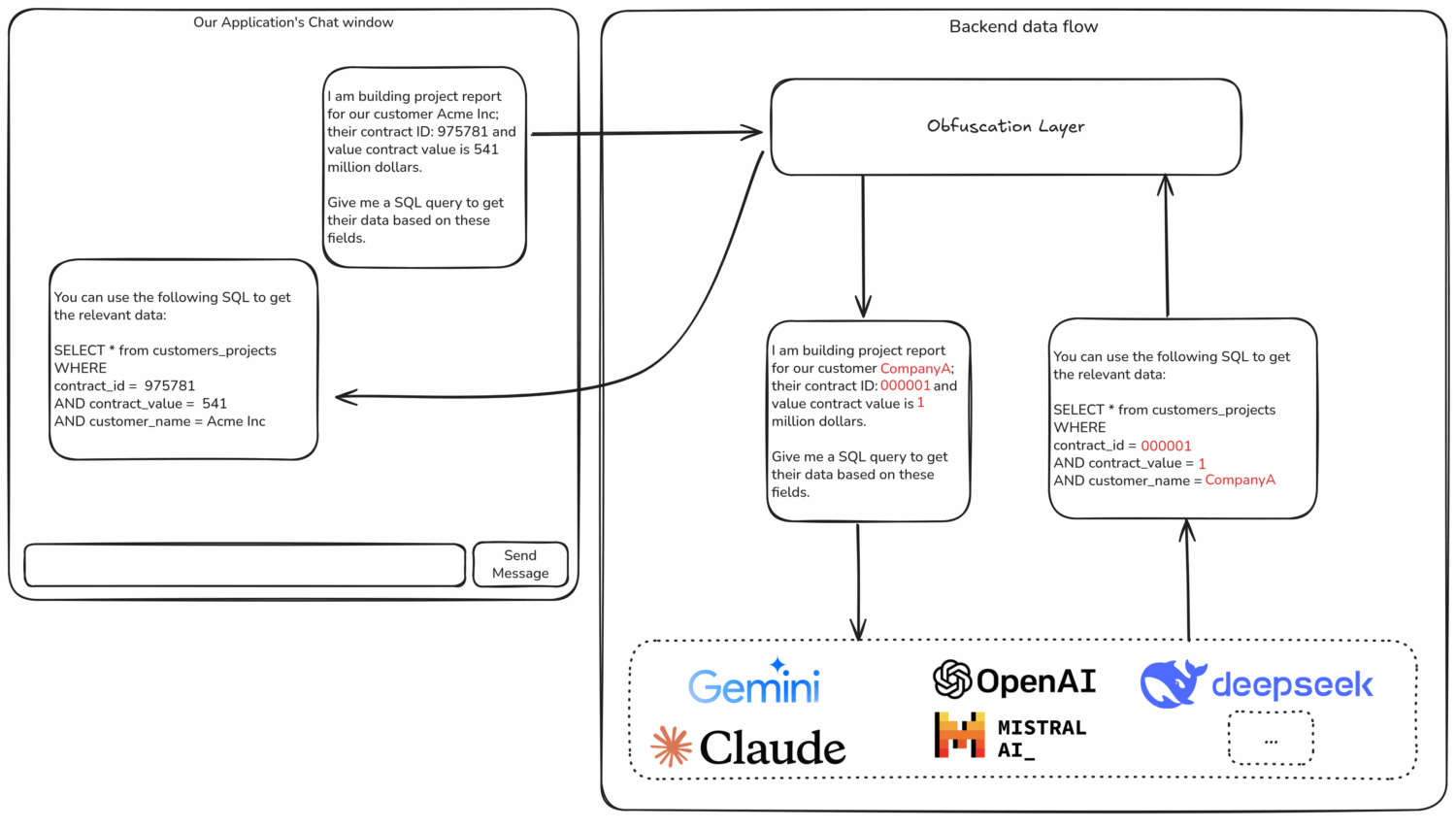
2. Self-hosted Models On-Premises
Running AI models on-premises is often seen as the gold standard for data security and control. In this approach, your organization hosts and maintains the models entirely within your internal data centers. No data is transmitted outside your secure network boundaries.
The advantage of this approach lies in its complete isolation from third-party infrastructure. Organizations retain full control over data flows, access permissions, and model behavior. This makes it well-suited for use cases involving classified, proprietary, or personally identifiable data where the consequences of exposure are high.
However, building AI infrastructure in-house demands substantial upfront investment in hardware, storage, and technical expertise; along with ongoing operational costs for system maintenance. Even after this huge investment, self-hosted open-source models generally lag behind state-of-the-art models in accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, latency and capacity limitations can pose significant challenges for wall-to-wall deployment of self-hosted models in large-scale applications.
3. Confidential Computing in the Cloud
Entrusting third-party AI providers with highly sensitive data is often challenging. However, Confidential Computing offers a promising approach that enables organizations to utilize cloud-based models without relying on trust alone. Confidential Computing is an emerging technology that protects data throughout its entire lifecycle, including during processing. By leveraging hardware-based Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), Confidential Computing ensures that data remains encrypted not only at rest and in transit but also while in use. For a deeper understanding, please refer to our educational blog on Confidential Computing.
However, this approach is still maturing. Not all cloud providers offer robust support, and some workloads may experience performance trade-offs. Integration with existing systems can be complex, requiring careful alignment of hardware, operating systems, and AI frameworks. Despite these challenges, Confidential Computing represents a meaningful step forward for secure AI in the cloud.
4. Role-Based Access and Policy Enforcement
Robust access control policies are essential for managing how, when, and by whom AI systems are used. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that different users, including engineers, analysts, or executives, interact with the system according to their specific responsibilities and data clearance.
These controls prevent accidental misuse and can align AI interactions with existing security policies. In regulated environments, enforcing data access policies at both the infrastructure and application level is critical to meeting audit and compliance requirements. For example, with RBAC, we can ensure that AI is only able to reference the document to which the current user has access. We can also create guardrails to monitor if a user is requesting information beyond the scope of their duties and alert security teams about the same.
5. Minimizing Data Scope
We have already discussed about minimizing data scope in Adam’s security features blog.
To summarize, AI is only allowed access to data after manual approval from the data source administrator. A fine-grained data access control system can ensure we redact any sensitive information while providing all relevant information to AI. This technique reduces the potential attack surface and prevents unintentional exposure of unrelated or sensitive content.
However, while limiting scope reduces risk, it may also restrict the AI’s ability to draw broader insights. There is often a trade-off between precision and depth. As such, organizations must carefully design AI workflows to ensure relevant context is included without overexposing information.
6. Monitoring, Logging, and Auditing
Monitoring and logging are indispensable tools for building trust in AI systems. By recording how models are used, what data they access, and what outputs they produce, organizations gain visibility into system behavior. This is essential for detecting misuse, investigating anomalies, and demonstrating compliance.
Audit trails also allow organizations to assess model performance and fairness over time. In sensitive environments, logging can help enforce internal policies and serve as evidence in the event of regulatory review or incident response. The challenge lies in striking the right balance. Logging too little reduces visibility; logging too much risks exposing sensitive data in the logs themselves. Proper log sanitization, access control, and retention policies must be part of the system design.
Conclusion
Adopting AI in highly regulated environments demands a thoughtful security strategy. In this blog, we explored multiple approaches to secure AI deployments. The strategies discussed are not mutually exclusive and in practice, a well architected solution will often combine several of these approaches, tailored to the specific risks and regulatory demands of your organization.
However, successfully using these techniques requires deep knowledge and experience. At SMS, we have invested in building this expertise. If you want help tailored to your requirements to introduce AI securely in your organization, please reach out to us at [email protected].